AI with JavaScript & Node.js full syllabus
Module 1: Foundations of AI With JavaScript
Goal: Learn the basics of Artificial Intelligence and understand why JavaScript (with Node.js) is a good choice for building AI-powered apps.
Topics:
1. What is Artificial Intelligence?
- AI means teaching computers to think, learn, and make decisions like humans.
- Example: Chatbots, recommendation systems (like Netflix), or voice assistants (Alexa, Siri).
2. Types of AI
- Narrow AI → Focused on one task (e.g., spam filter, Google Translate).
- General AI → Can think and learn like humans (still in research).
- Super AI → Smarter than humans (future concept).
3. Real-World Use Cases of AI
- Self-driving cars
- Fraud detection in banks
- Personalized ads & recommendations
- Smart assistants like Alexa/Google Assistant
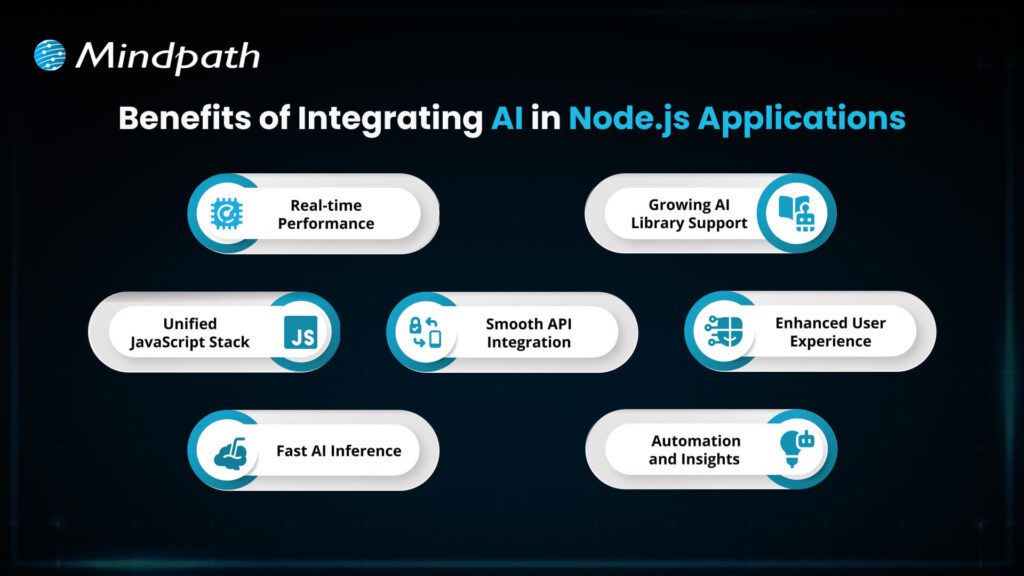
4. Why JavaScript for AI?
- JavaScript is everywhere (web, mobile, backend).
- Huge ecosystem of libraries for AI/ML.
- Easy to integrate AI into websites and apps.
- Works well with Node.js for server-side AI applications.
5. Introduction to Node.js & npm
- Node.js → Lets you run JavaScript outside the browser (server-side).
- npm (Node Package Manager) → Helps you install pre-built libraries and tools.
- Example: You can install
brain.js(a neural network library) with just one command.
6. Setting Up Your Project
- Install Node.js & VS Code.
- Initialize your project →
npm init. - Add AI-related libraries later (e.g.,
brain.js,tensorflow.js). - Use Git for version control (track your code changes).
Mini Project: Your First Chatbot
- Create a simple command-line chatbot.
- The chatbot will take user input and reply with predefined responses.
- Example:
- User: “Hi” → Bot: “Hello, how are you?”
- User: “Bye” → Bot: “Goodbye, see you soon!”
This small project will help you understand:
✔ How JavaScript reads input and gives output
✔ The logic behind simple AI interactions
✔ How to run JS code with Node.js
Module 2: Core AI with JavaScript
Goal:Build a strong foundation in modern JavaScript so you can use it effectively in AI projects.
Topics:What You’ll Learn
- ES6+ Features: Understand let and const for variables, arrow functions for writing shorter code, and template literals for easy string handling.
- Arrays & Objects: Learn how to loop through arrays, use map and filter for transforming data, and handle objects effectively for structured data.
- Promises & Async/Await: Discover how to manage asynchronous tasks like data fetching without blocking the program.
- Fetch API: Practice fetching data from external sources such as APIs, which is useful in AI and data-driven applications.
- Working with JSON: Learn how to store, read, and process data in JSON format, which is the standard for AI datasets.
- Error Handling: Explore how to handle errors gracefully so that your applications remain reliable and user-friendly.
Project: Data Fetcher App
At the end of this module, you’ll build a simple app that fetches data from an API. For example, you can create a weather app that shows live updates or a news app that pulls the latest headlines. This project will teach you how to connect JavaScript with real-world data—just like how AI tools fetch and process large datasets.
Module 3: Math & Logic for AI with JavaScript

Goal: Understand the math and logical thinking behind AI, and learn how to implement these concepts using JavaScript. This module helps you build the foundation for writing simple AI algorithms.
Topics:
- Arrays and Matrix Operations in JS
Learn how to use arrays in JavaScript not just for storing data but also for performing operations similar to mathematical matrices. This will prepare you to handle the kind of data structures often used in AI. - Probability and Statistics Basics
Understand simple concepts like probability, mean, median, and variance, which are essential for AI models that deal with predictions and randomness. - Normalization and Scaling
Learn how to bring data into a consistent range so that AI algorithms can make accurate comparisons. For example, scaling data between 0 and 1. - Random Number Generation
Discover how to generate random numbers in JavaScript. This is useful in creating training datasets, simulations, or testing scenarios in AI. - Creating Simple Algorithms in JS
Start writing small algorithms step by step. Learn how logic and conditions can be combined to make decisions automatically.
Mini Project
Rock-Paper-Scissors Bot
Build a simple game where your bot plays Rock-Paper-Scissors with the user. Over time, the bot will try to adapt to the player’s choices and respond smarter, showing how logic and probability can create adaptive behavior.
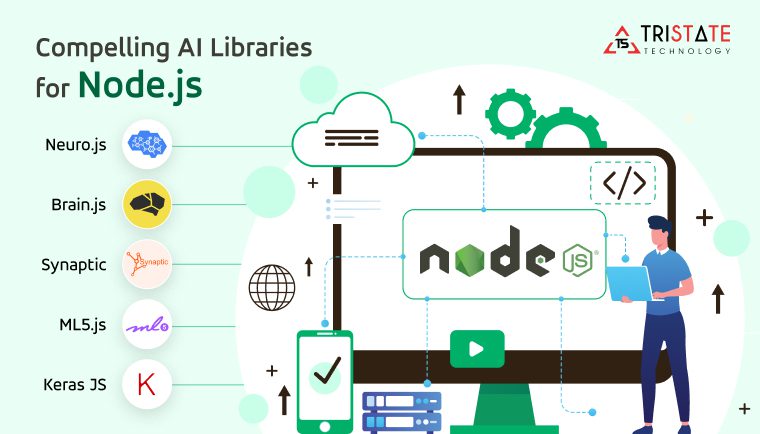
Module 4: Machine Learning in JavaScript
Goal: The main purpose of this module is to help you understand how machine learning actually works and how you can build ML models directly inside JavaScript using popular libraries. By the end of this module, you won’t just know the theory, but you’ll also build your first real ML project in JS.
Libraries Covered:
- TensorFlow.js – The most powerful library that brings deep learning into JavaScript. You can run ML models in the browser or Node.js without needing Python.
- Brain.js – A lightweight library focused on neural networks. Great for beginners who want to test simple models quickly.
- Synaptic – Another library for neural networks that is simple and flexible for experimentation.
- ml5.js – A beginner-friendly wrapper around TensorFlow.js that makes machine learning super easy with simple APIs.
Topics:
- What is Machine Learning?
- You’ll learn how ML allows computers to learn patterns from data instead of being hard-coded.
- Training vs Testing Data
- You’ll understand why we split data into training sets (for the computer to learn) and testing sets (to check if it has learned correctly).
- Supervised vs Unsupervised Learning
- Supervised Learning: You give the model data with correct answers (labels) so it can learn patterns.
- Unsupervised Learning: The model finds patterns in unlabelled data by itself (like grouping similar items).
- Loading Datasets in JavaScript
- Learn how to import datasets into your JS project (for example, CSV or JSON files) and prepare them for training.
- Training Simple Models
- You’ll train basic models such as:
- Linear regression (predicting numbers, like house prices)
- Simple classification (deciding between categories, like spam or not spam)
Project:
You’ll build a linear regression model in JavaScript that predicts the price of a house based on factors like size (square feet), location, or number of rooms.
Steps you’ll follow:
- Load sample housing data into your project.
- Preprocess the data by scaling and normalizing it.
- Build a simple neural network with TensorFlow.js.
- Train the model on historical data.
- Test the model by giving it new input (e.g., “house with 3 rooms and 1200 sq ft”) and see the predicted price.
By doing this project, you’ll see how math, data, and code all come together to create something practical and useful with AI.
Module 5: Working with TensorFlow.js(AI with JavaScript)
Goal:The goal of this module is to understand how to build deep learning models directly in the browser or using Node.js with the help of TensorFlow.js. By the end of this module, you will be able to create, train, evaluate, and deploy AI models using JavaScript.
Topics:
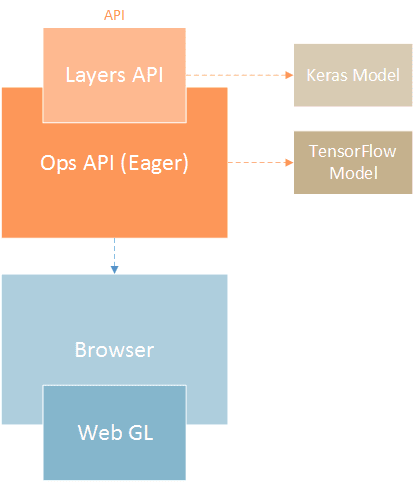
What is TensorFlow.js?
- A JavaScript library for machine learning.
- Works in both the browser and Node.js.
- Lets you use pre-trained models or build your own.
Setting up environments:
- Browser: Easy setup, good for lightweight apps and experiments.
- Node.js: Installed using npm, better for large-scale AI projects.
Understanding Tensors:
- Core building block of TensorFlow.js.
- A tensor is like a multi-dimensional array that holds data.
- Example:
- Single number → 0D tensor
- List of numbers → 1D tensor
- Table (rows & columns) → 2D tensor
Creating a Neural Network:
- Neural networks are made of layers.
- Common layers: Dense layers, Activation functions (ReLU, Softmax).
- Optimizers like Adam help in better training.
Training and Evaluating Models:
- Train a model by feeding it data multiple times.
- Example: Handwritten digit dataset used for practice.
- Evaluation is done using test data to check accuracy.
Saving and Loading Models:
- Trained models can be stored locally or in browser storage.
- Models can be reused without training again.
- Useful for deployment and sharing.
Project: Handwriting Digit Recognizer (MNIST Dataset):
- Dataset has thousands of handwritten digits (0–9).
- User draws a digit on screen.
- Model predicts which number it is.
- Real-world use cases: OCR, handwriting recognition apps.
Module 6: Natural Language Processing (NLP) with Node.js
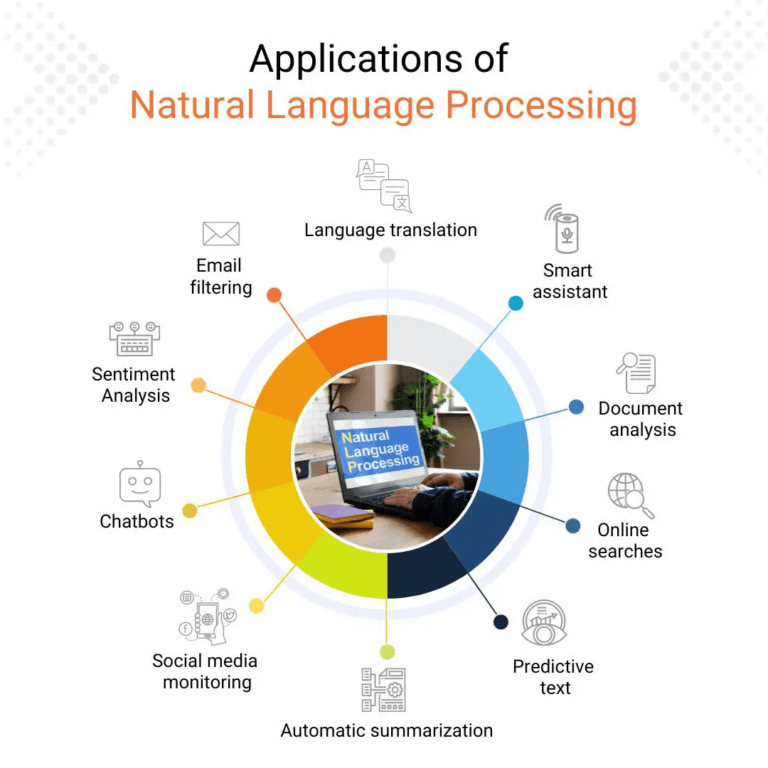
Goal: Learn how to make your apps understand and respond to human language — like chatbots, personal assistants, and voice-powered tools.
Libraries:
compromise → For easy text processing like extracting dates, names, and numbers.
natural → For tokenization, stemming, and sentiment analysis.
nlp.js → For building conversational agents and chatbots with multilingual support.
Topics:
- Tokenization & Stemming
- Breaking down sentences into words (tokenization).
- Reducing words to their base form (stemming/lemmatization).
- Example: “running” → “run”.
- Sentiment Analysis
- Understanding emotions in text (positive, negative, or neutral).
- Example: “I love this course” → Positive sentiment.
- Named Entity Recognition (NER)
- Identifying important words like names, places, organizations, dates.
- Example: “Elon Musk founded SpaceX in 2002” → (Person: Elon Musk, Organization: SpaceX, Date: 2002).
- Creating Conversational Agents
- Building chatbots that respond naturally.
- Handling user queries, context, and multiple conversation flows.
- Example: A customer support bot for FAQs.
- Voice-based Input
- Using Web Speech API for browser-based voice recognition.
- Or integrating Google Cloud Speech-to-Text API for more powerful voice understanding.
- Example: Say “What’s the weather today?” and get an automated spoken/text response.
Project: Voice-Activated Personal Assistant
By the end of this module, you’ll build a mini Jarvis-like assistant that:
- Listens to your voice commands.
- Converts speech into text.
- Understands meaning using NLP (tokenization, sentiment, NER).
- Responds back with useful answers (like weather updates, reminders, or jokes).
- Can even be extended to control apps, search Google, or send messages.
Module 7: AI APIs & Cloud AI Integration(AI with JavaScript)
Goal: Learn how to connect your apps with powerful cloud-based AI services like OpenAI, Google Cloud, HuggingFace, and Microsoft Azure to add features such as chatbots, voice recognition, and smart text analysis.
Platforms:
- OpenAI → Tools like ChatGPT for conversations and Whisper for speech-to-text.
- Google Cloud AI → Vision, NLP, Translation, Speech, and more.
- HuggingFace APIs → Pre-trained models for text, images, and transformers.
- Microsoft Azure AI → Cloud services for language, speech, vision, and decision-making.
Topics:
- REST API Basics
- Learn how APIs work for communication between your app and cloud AI services.
- Example: Sending a question to ChatGPT and getting a text response.
- Working with API Keys Securely
- Every service requires a unique key to authenticate.
- Learn how to store keys safely using environment variables instead of hardcoding them.
- Sending & Receiving AI Data
- Use HTTP methods (POST, GET) to send requests.
- Example: Send user’s text to Google Cloud NLP → receive analyzed sentiment back.
- Handling JSON Responses
- AI APIs usually return data in JSON format.
- Learn how to parse, extract, and display results in your app.
- Example: Extract “sentiment: positive” or “answer: Yes, that’s correct.”
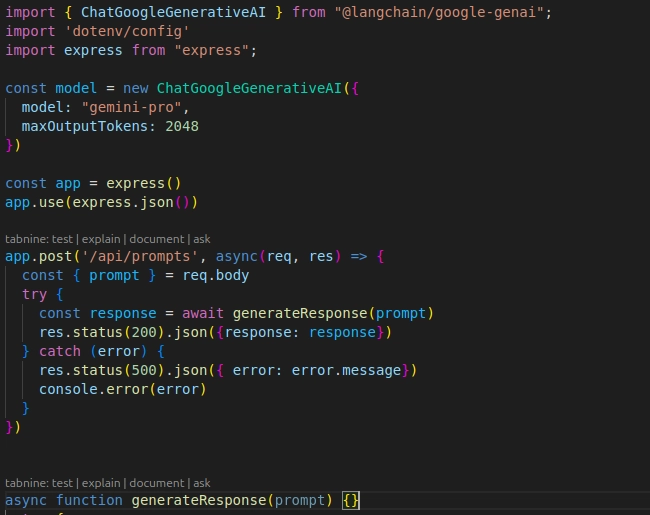
Project: ChatGPT-powered Q&A Bot (Node.js + Express)
By the end of this module, you’ll build a Q&A chatbot that:
- Runs on a Node.js + Express server.
- Accepts user questions via a web form or API endpoint.
- Sends the question to ChatGPT through the OpenAI API.
- Receives and displays the answer in real-time.
- Can be extended with Google Cloud APIs (like adding voice input using speech-to-text).
Example Flow:
- User types: “What is machine learning?”
- Server sends the question to ChatGPT API.
- ChatGPT returns a JSON response with the answer.
- Bot displays: “Machine learning is a method of teaching computers to learn from data.”
Module 8: Real-Time AI Applications(AI with JavaScript)
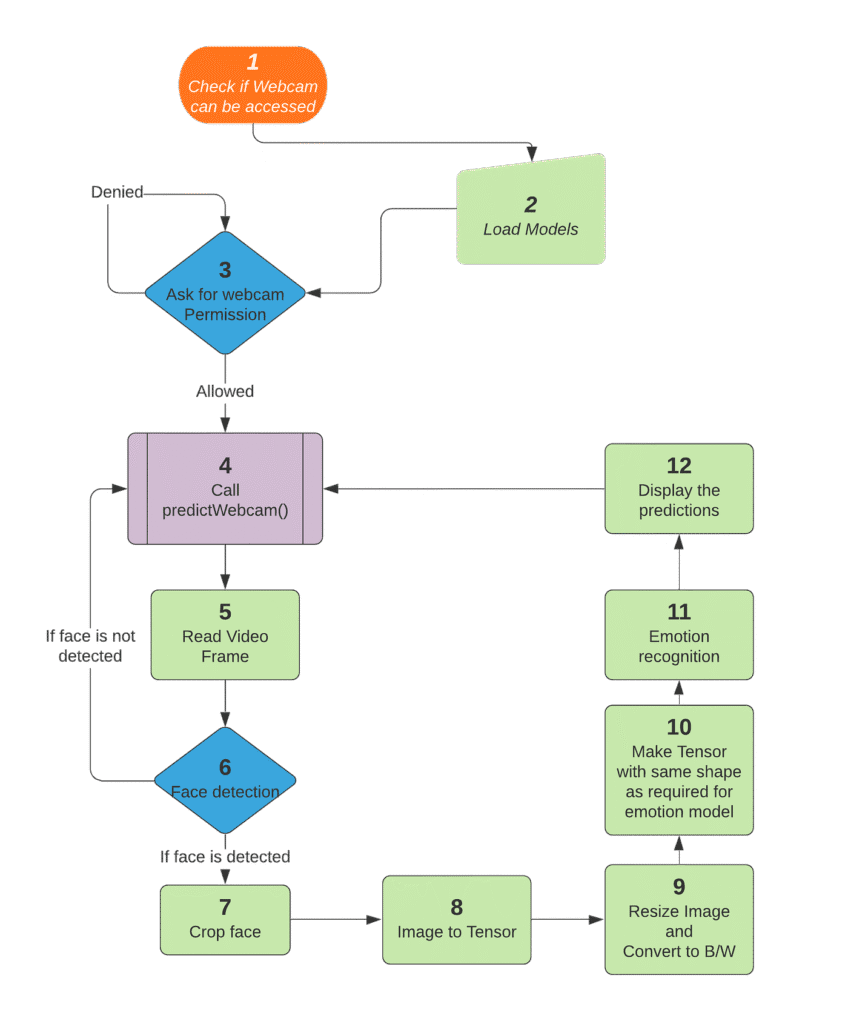
Goal: Learn how to build interactive AI projects that work instantly in real time, such as detecting emotions from a live webcam feed or updating a dashboard with AI-powered insights.
Topics:
- Real-time Webcam Input with JavaScript
- Learn how to access the user’s webcam directly from the browser using JavaScript.
- Capture video frames live and feed them into an AI model.
- Example: Taking a live camera stream to detect if a person is happy, sad, or neutral.
- Using WebSockets (socket.io)
- Understand how WebSockets allow instant communication between the browser and server.
- Use socket.io for sending and receiving real-time data.
- Example: A live chat or dashboard that updates instantly without refreshing the page.
- Integrating with TensorFlow.js Models
- Load pre-trained TensorFlow.js models in the browser.
- Use them on live webcam input for predictions.
- Example: Emotion detection model analyzing each frame from the webcam.
- Live Emotion Detection
- Detect human emotions like happy, sad, angry, surprised from video input.
- Visualize emotions instantly on screen with labels or emojis.
- Example: If you smile, the app shows “Happy 😀” in real time.
- Browser-based AI Dashboards
- Build dashboards that show results from your AI models.
- Example: A dashboard that displays live emotion stats (like “60% Happy, 30% Neutral, 10% Sad”).
Project: Real-Time Emotion Detection App (Webcam + TensorFlow.js)
By the end of this module, you’ll create a real-time web app that:
- Opens the user’s webcam in the browser.
- Continuously captures video frames.
- Sends frames into a TensorFlow.js model trained for emotion detection.
- Shows the detected emotion instantly on the screen.
- Displays results on a live dashboard (like a chart of emotions).
Example Flow:
- User looks into webcam.
- JavaScript captures video frames.
- TensorFlow.js model analyzes each frame.
- Detected emotion (e.g., “Happy”) is shown instantly.
- Dashboard updates live with emotion stats.
Module 9: Hosting, Deployment & Optimization
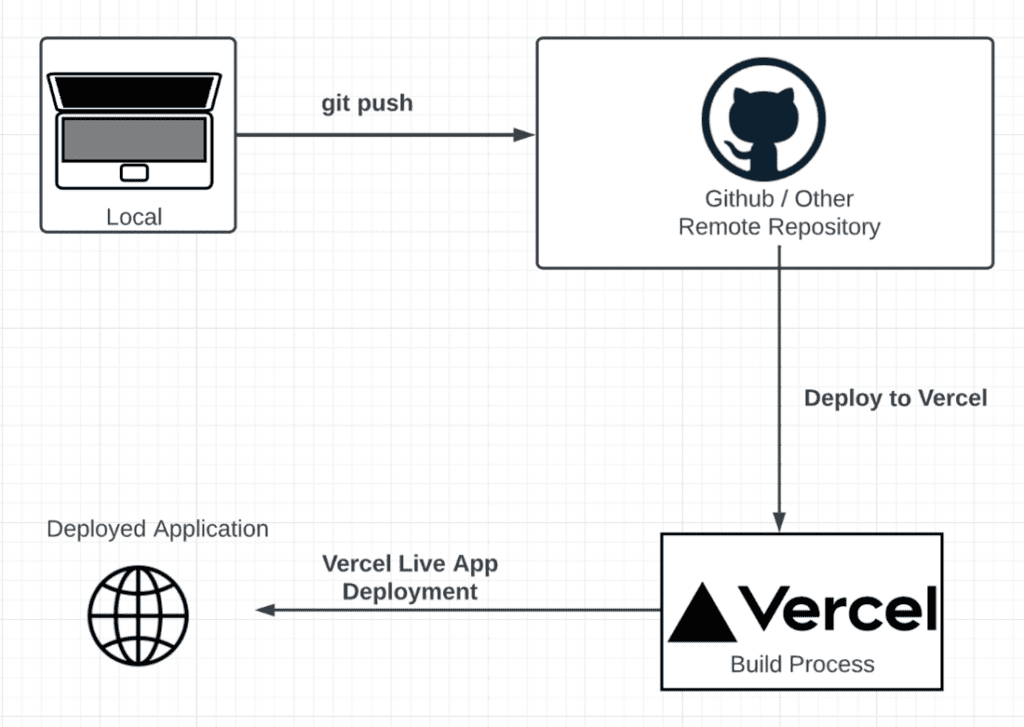
Goal: Learn how to take the AI apps you built and make them production-ready so anyone in the world can access and use them.
Topics:
- Hosting with Vercel, Netlify, or Heroku
- Learn how to put your web apps online.
- Vercel & Netlify → Best for front-end apps (React, Next.js, static sites).
- Heroku → Good for full-stack apps and quick backend deployment.
- Example: Deploy your AI dashboard so friends can open it with just a link.
- Express.js Server Deployment
- Host backend services that power your AI apps.
- Deploy APIs made with Node.js + Express so they can connect with your front-end.
- Example: A chatbot server that handles API calls to ChatGPT.
- Environment Variables
- Keep your API keys and sensitive data safe by using
.envfiles. - Never expose keys directly in code.
- Example: Store your OpenAI API key in
process.env.OPENAI_KEYinstead of hardcoding it.
- Keep your API keys and sensitive data safe by using
- Model Optimization (Quantization)
- Reduce the size of your AI models to make them faster and lighter.
- Quantization changes models from 32-bit to smaller formats without losing much accuracy.
- Example: Making a TensorFlow.js model run smoothly even on mobile.
- Caching AI Results
- Save repeated AI responses so you don’t waste time and API credits.
- Example: If a user asks the same question again, fetch the stored response instead of re-calling the API.
- Handling Errors & Fallback Models
- Build your app to handle downtime or errors gracefully.
- Example: If the AI API is unavailable, show a helpful message or use a simpler backup model.
Project: Deploy Your Own AI Chatbot on a Public Domain
By the end of this module, you’ll:
- Take your ChatGPT-powered chatbot.
- Host the front-end on Vercel or Netlify.
- Host the backend API on Heroku or Vercel Functions.
- Secure it using environment variables.
- Optimize responses with caching.
- Add error handling for smooth user experience.
- Share a public URL so anyone can chat with your bot worldwide.
Module 10: Final Capstone Projects (AI with JavaScript)
Goal: Bring everything you’ve learned together and build complete AI products from scratch. These projects will showcase your skills and can be used in your portfolio or even scaled into real-world apps.
Ideas:
- AI-Powered Resume Screener
- Build a tool that scans resumes and highlights the most relevant skills for a job.
- Use NLP techniques like keyword extraction and sentiment scoring.
- Example: Upload a resume → AI suggests if the candidate is a good fit for a “Digital Marketing” role.
- ChatGPT Clone with Custom Training
- Create your own chatbot similar to ChatGPT.
- Train it on a custom dataset (like your company FAQs or personal notes).
- Example: A chatbot that answers only about “AI Courses” or “Company Policies.”
- Visual Recognition System in Browser
- Use TensorFlow.js to build an image recognition system that works directly in the browser.
- Detect objects, animals, or even handwritten digits in real-time.
- Example: Point your webcam at a cat → AI says “Cat detected 🐱.”
- Music Genre Predictor using ML
- Train a machine learning model to classify songs into genres (pop, rock, jazz, hip-hop, etc.).
- Input: audio features (tempo, pitch, rhythm).
- Output: predicted genre.
- Example: Upload a song → AI predicts: “This is 80% Pop, 15% Rock, 5% Jazz.”
Why This Module is Important
- You’ll apply all skills (NLP, computer vision, APIs, deployment, real-time AI).
- You’ll learn to handle end-to-end product building → from coding to hosting.
- You’ll have portfolio-ready projects to show employers or clients.
Here’s a great Coursera course focused on applying AI in JavaScript and web development:


